
Industry news|2022-03-02| admin
All parts in a machine cannot exist in isolation, they must be connected with other parts in some way, which gives rise to mechanical connections.
Mechanical connections can be divided into two categories: one is the connection that can have relative motion between the connected parts when the machine is working, which is called mechanical dynamic connection, such as various kinematic pairs learned in mechanical principles; the other is When the machine is working, the connection where the connected parts are not allowed to move relative to each other is called a mechanical static connection.
Mechanical static connections can also be divided into two categories: detachable connections and non-detachable connections.
A detachable connection is a connection that can be detached without destroying any part of the connection. Common ones are threaded connection, key connection, spline connection and pin connection.
A non-removable connection is a connection that must destroy at least one part of the connection in order to be disconnected. Common ones include riveting, welding and gluing.
In addition, there is an interference fit connection that can be made detachable or non-detachable, which is also often used in machines.
The threaded connection is simple in structure, easy to use, and can be disassembled and assembled frequently, and is the most widely used. Key connection, spline connection and interference connection are often used for the connection between the shaft and the parts on the shaft - the shaft-hub connection.
1. Types and applications of threads
The thread has an inner thread and an outer thread, which together form a screw pair for connection or transmission. According to the shape of the parent body, it is divided into cylindrical thread and conical thread; according to the tooth shape, it is divided into triangular thread, rectangular thread, trapezoidal thread and serrated thread. According to the direction of the thread helix, it is divided into left-handed and right-handed threads. In addition, there are single-line and multi-line points for threads. Triangular threads are mainly used for coupling, while rectangular, trapezoidal and zigzag threads are mainly used for transmission, of which all but rectangular have been standardized. The basic dimensions of standard threads can be found in the relevant standards.
There are many kinds of common threads, which can be divided into the following two categories according to their uses:
1. Connection thread
The tooth shape of the connecting thread is triangular, which is characterized by large equivalent friction angle, good self-locking and high strength. Common types include ordinary thread, pipe thread and conical thread.
The tooth angle a=60° of the common thread, and there is a radial gap after the inner and outer threads are screwed together. Ordinary threads of the same nominal diameter are divided into coarse thread and fine thread ordinary thread according to the difference in pitch. Fine-pitch ordinary threads are often used for cutting parts with coarse-pitch threads that have a great influence on strength (such as shafts, tubular parts) or connections subject to shock vibration and variable loads, and can also be used as adjustment threads for fine-tuning mechanisms.
The profile angle of the pipe thread is a=55°, the crest has a large rounded angle, and there is no radial clearance after the internal and external threads are screwed together to ensure the tightness of the screwing. Generally used for connections in piping systems.
The tapered thread is similar to the tapered pipe thread, but the profile angle a=60°, and the thread crest is flat. It is widely used in fuel, oil, water and gas delivery pipeline systems for automobiles, tractors, aviation machinery and machine tools.
2. Transmission thread
Compared with the connecting thread, the tooth profile angle a of the transmission thread is smaller, so its transmission efficiency is high. According to the different tooth types, the types of transmission threads are rectangular thread, trapezoidal thread and serrated thread.
The tooth profile of the rectangular thread is square, and the profile angle a=0°. Its transmission efficiency is higher than other threads, but the root strength is weak, and the gap is difficult to compensate after thread wear, which reduces the transmission accuracy, and has been gradually replaced by trapezoidal threads. Rectangular threads are not yet standardized.
The profile of the trapezoidal thread is an isosceles trapezoid, and the profile angle a=30°. Compared with the rectangular thread, the transmission efficiency of the trapezoidal thread is slightly lower, but its craftsmanship is good, the root strength is high, and the alignment is good. Such as split nut, the gap can be adjusted after wear, it is the most common transmission thread.
The tooth shape of the serrated thread is an isosceles trapezoid, the half angle of the tooth shape of the working face is β=3°, and the half angle of the tooth shape of the non-working face is 30°. The root of the external thread has a larger fillet to reduce stress concentration. After the internal and external threads are screwed together, there is no gap at the major diameter, which is convenient for centering. This kind of thread has the characteristics of high transmission efficiency of rectangular thread and high strength of trapezoidal thread root, but it can only be used in the transmission screw with one-way force.
Third, the main parameters of the thread
The main parameters of the thread are described below by taking the common thread of the widely used cylindrical pin as an example.
1. Major diameter d—the diameter of the imaginary cylindrical surface that coincides with the crest of the external thread or the crest of the internal thread or the bottom of the internal thread, also known as the nominal diameter (except for pipe threads).
2. Minor diameter d—the diameter of the imaginary cylindrical surface that coincides with the bottom of the external thread or the top of the internal thread, and is often used as the calculated diameter of the dangerous section in the strength calculation.
3. Pitch diameter d---the diameter of the cylinder where the tooth thickness of the thread is equal to the width between the teeth.
4. The number of lines n-----the number of helical lines of the thread. In order to facilitate manufacturing, generally n is less than or equal to 4.
5. Pitch P-----the axial distance between the corresponding two points on the adjacent two tooth profiles of the thread.
6. Lead S------ the axial distance between two points corresponding to two adjacent tooth profiles on the same helix, S=nP.
7. Thread lift angle φ------ the angle between the tangent of the helix on the middle diameter cylinder and the plane perpendicular to the thread axis, the calculation formula is:
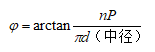
8. Tooth profile angle a------In the axial section, the angle between the two sides of the thread profile. The angle between the measured edge of the thread profile and the vertical line of the thread axis is called the profile half angle β. For symmetrical tooth shapes such as triangles and trapezoids, β=a/2.
9. Thread contact height h------ On the tooth profiles of two mutually matched threads, the distance of the overlapping part of the teeth in the direction perpendicular to the thread axis.
